The government recently released the ACT Workers Compensation Review of Scheme Performance report (the Report).
The Report analyses the performance of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) Workers Compensation scheme (the Scheme) and the environment it’s operating in, helping the government and industry set premiums and manage risks.
To help our partners and customers understand the Report and what it means to them, we’ve summarised important information including:
- Scheme performance and recommended premium rates
- Claims experience and trends
- Economic and environmental factors
Key findings and recommendations
- The Report recommended an average premium rate for 2020/21 of 2.33% of wages, a decrease of 0.16% from 2019/20
- Recommended premium rates for industries at the ANZSIC Class level ranged between 0.28% to 15.36% of wages
- Just under $134 million of claim payments were made in 2018/19, consistent with 2017/18
- The Report predicted a non-nil claim frequency of 0.309 claims per $1 million of wages for the 2020/21 policy year, 9% lower than adopted for the 2019/20 policy year
- Factors including wages and workforce size have a direct impact on the Scheme however the Report noted the COVID-19 pandemic and related economic uncertainties had not been a consideration in projections and recommended rates
Scheme performance and premium rates
Historical premium rates and scheme performance
The Report showed the Scheme has remained stable in recent years – with premiums adequately supporting customers and claims costs in addition to insurer and brokerage expenses and margins.
Historical risk premium (premium needed to cover claims only) reflected this, showing consistency in the five years to 2017/2018 and a modest decrease in 2018/19. Part of this change was likely linked to a shift across ACT towards wages in lower risk industries as well as an improvement in claim frequency across the board.
The Report also revealed in 2018/19 around 17,800 Scheme policies were written, covering $10.6 billion in wages. In line with this, a total $205 million of premium was collected.
Risk premiums by accident year
.jpg)
Source: ACT Workers Compensation Review of Scheme Performance, 2020
Projected average premium rate
The Report recommended an average 2020/21 premium rate of 2.33% of wages.
This is a decrease of 0.16% from the 2019/2020 recommended rate (a 6% proportionate decrease) and means customers may see a modest drop in upcoming premiums depending on industry class and measures set by individual insurers.
Key drivers of this recommendation included:
- Allowance for one year’s superimposed inflation (to 2020/21) – increase of 0.03%
- Claims cost changes – decrease of 0.30%
- Economic assumptions – increase of 0.07%
- Expense loadings – increase of 0.05%
Notably, the Report also estimated the average renewal date for workers’ compensation policies in the ACT is mid-September. This was based on past patterns of wages covered and earned wages.
Recommended premium rates for industries, calculated at the ANZSIC Class level, were also provided in the Report. These ranged between 0.28% to 15.36% of wages and were developed based on the average recommended rate as well as wages, risk factors and claims data specific to each class.
Importantly, the Report noted expense and profit requirements were different for each insurer and the risk experience of an employer would also be a key factor in determining actual premiums and rates.
Claims experience and trends
Claims frequency, costs and size
The Report revealed just under $134 million of claim payments were made in 2018/19, consistent with the previous year and an important consideration in recommended rates. The mix of payments shifted slightly towards statutory benefits.
New non-nil claims (claims with no payments) decreased slightly to 3,252 over 2018/19 when compared to 2017/18. Lost time claims were however up by 1% - with 2112 new lost time claims reported.
The Report also showed the Scheme’s non-nil claim frequency per $ million wages has steadily reduced since 2010/11, to an estimated 0.309 claims per million wages for the 2018/19 accident year. Wage growth has driven these frequency reductions.
Projected claims
Based on historical data, claims drivers and economic assumptions, the Report predicted a non-nil claim frequency of 0.309 claims per $ 1 million of wages for the 2020/21 policy year, 9% lower (adjusting for actual inflation) than adopted for the 2019/20 policy year.
It projected a total of 3,447 claims and estimated the average claim size per non-nil claim would be $42,340 for the 2020/21 policy year, decreasing slightly from the previous year’s average size.
Injury trends
The Report included an analysis of injury claims (only including primary injury type). Noatbly, injury claims make up around 70% of total claim numbers, with musculoskeletal claims representing a significant 20%.
Since 2015 the proportion of mental health claims has gradually increased from 4.8% to 5.9%, while the proportion of musculoskeletal claims has been variable.
It’s important to note, mental health and musculoskeletal claims have higher average costs than average injury claims, so can have a greater impact on the Scheme and premiums.
Claims by injury type
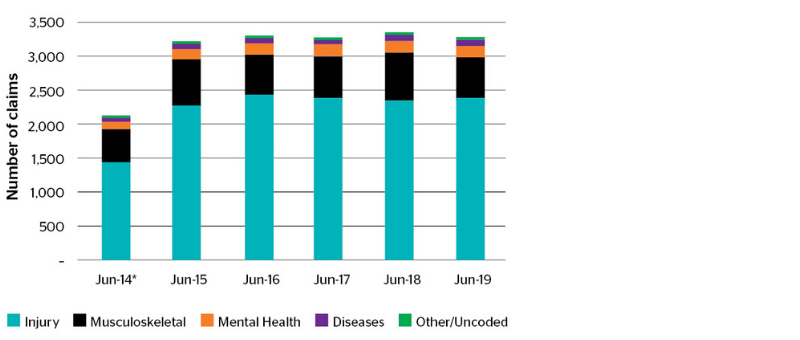
*June 2014 has only nine months of coding
Source: ACT Workers Compensation Review of Scheme Performance, 2020
Economic and other influencing factors
Benefit changes
The Report noted the Workers Compensation Amendment Bill 2017 has resulted in two changes to the way benefits are structured:
- Weekly benefits no longer align with the Commonwealth retirement age (previously 65) but instead would gradually increase
- Death benefits now align with the Comcare scheme
These changes (and resulting claims costs) were considered in the 2020/21 recommended premium rates.
Wages and economic growth
The Report noted written wages in 2018/19 were higher than expected, driven by stronger than expected workforce growth. For example, there was significant wage growth in the professional/scientific sector. In line with this, earned wages grew by 4% to $10.6 billion in 2018/19.
The Report based workforce growth estimations for 2020/21 on an assumption of 1.0% per annum economic growth to 2020/21. This was based on market forecasts available at the time of the review.
The Report predicted wage inflation of 3.0% per annum between 2018/19 and 2020/21. In line with this, the Report projected written wages of around $11.5 billion in the 2020/21 policy year.
Economic impact and COVID-19
Economic activity and employment rates have a direct impact on the Scheme’s performance, impacting return to work rates, wages and therefore premium pools and claims.
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused significant uncertainty around Australia’s economic future. The Report noted these uncertainties had not been considered in projections.
For more information specific to COVID-19 and its impact to Workers Compensation in the ACT please visit the ACT Government’s website.
Find out more
Read the full Report or visit the Government’s website to find out more about Workers Compensation in the ACT.
For more information on our Workers Compensation offering, or a personalised analysis of what the Report findings or recent changes might mean for your business, please get in touch with your QBE Business Relationship Manager or broker.
Download a pdf version of this guide
Please note this is a summary of selected information only. The full Workers Compensation Review of Scheme Performance report should be read to understand findings, projections and data in full context.
The advice in this article is general in nature and has been prepared without taking into account your objectives, financial situation or needs. You must decide whether or not it is appropriate, in light of your own circumstances, to act on this advice.
